Introduction to SLURM
26 May 2024
What is SLURM?
SLURM is an acronym for Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management
SLURM is a free and versatile tool that streamlines job scheduling and resource allocation on Linux-based clusters. Imagine having dozens or even hundreds of compute nodes – SLURM ensures efficient utilization by:
- Resource Allocation: Granting users exclusive or non-exclusive access to compute nodes for specific durations.
- Job Scheduling & Execution: Providing a framework for launching and monitoring jobs, often involving parallel processing techniques like MPI (Message Passing Interface).
- Queue Management: Maintaining a queue of submitted jobs, prioritizing them based on predefined rules, and ensuring fair access to resources => Resource contention
Why use SLURM?
- SLURM is an open-source Job Scheduler for small and large linux clusters and unix-like kernels
- SLURM is fault-tolerant and highly scalable cluster management system
- SLURM is relatively self-contained with the components it needs to run
What are Important components of SLURM?
slurmctld, the central controller monitoring all the compute nodes that are registered as part of the cluster. Typically this is run dedicated management nodeslurmd, the daemon that runs on each compute node
Picture Source: https://slurm.schedmd.com/arch.gif
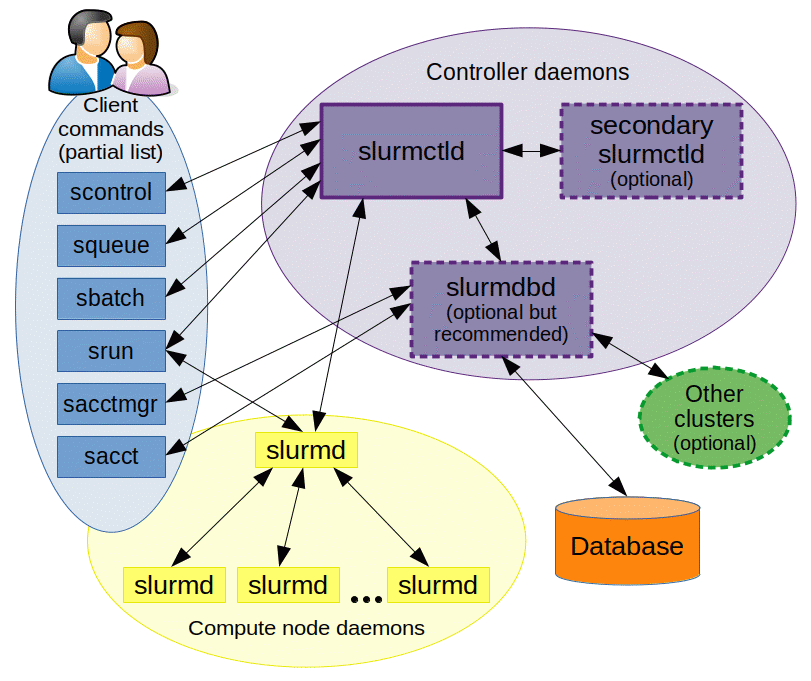
What are different entities in SLURM ?
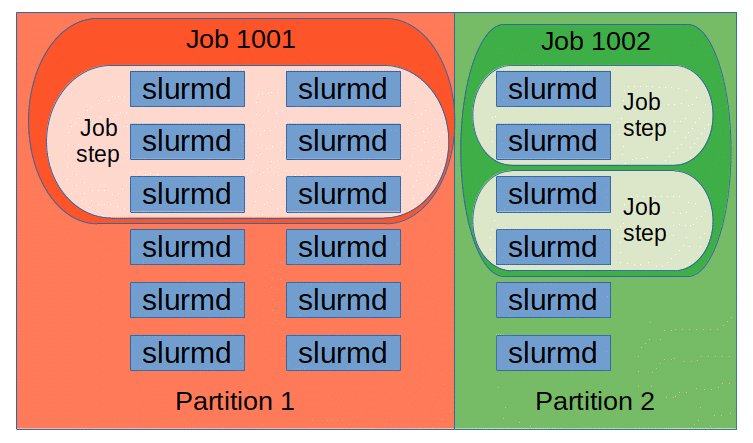
- Nodes - Actual Compute nodes
- Partitions - Logical grouping of nodes a.k.a
Job Queueswith an mix of constraints (job size limit / job time limit), priority - Jobs - Allocations of resources assigned to a user for a specified amount of time. Logical groups of job steps
- Job Steps - sets of tasks with in a job. Typically there are parallel tasks
Picture Source: https://slurm.schedmd.com/entities.gif
Finally the list of important commands
Ordered in the most frequently used or relevant
sbatch- to submit a job for eventual executionsrun- submit job for execution in real time. It could even be used to initiate job steps in real timescancel- to cancel a pending or running job step or job (all job steps)squeue- state of jobs/job stepssinfo- show the state of partitions and nodes as reportsview- GUI to display information for jobs/parititions and nodessstat- info about resource utilization by a running job/job stepsshare- info about fairshare usage. Only available in conjuction to priority/multifactor pluginsprio- details of the factors/components/constraints affecting a job's priorityscontrol- admin tool to view/modify the state of slurmsbcast- transfer a file between local storage on nodes with in a job allocation. This works like in a p2p fashion and simulates diskless nodes and improved performance relative to shared FSsattach- attach stdin / stdout / stderror along with sending signal to an already running jobsalloc- allocate resources in real time to the jobs. This spawns a shell with allocated resources andsruncommands with in this shell is used to launch parallel tasksacct- report job or job step information about active/completed jobs
Recommended exercise to go through SLURM demo on EC2 instance SLURM demo on AWS Ubuntu 22.04 EC2 instance





